What is Hip Bursitis?
Hip bursitis is a common condition that manifests as pain and discomfort around the outside of the hip joint. It occurs when the bursa, a small fluid-filled sac that cushions the bones, tendons, and muscles near the joints, becomes inflamed. The bursa reduces friction and provides smooth movement, but when irritated or inflamed, it can lead to significant pain and mobility issues. Hip bursitis often affects the outer part of the hip, and the pain can sometimes radiate down to the thigh.
How is Hip Bursitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing hip bursitis typically involves a combination of physical examination and medical history assessment. A physiotherapist or GP will ask about your symptoms, such as the location, duration, and intensity of your hip pain. They may also ask about any recent injuries or activities that could have contributed to the condition.
During the physical examination, your physiotherapist or GP will apply pressure to the hip area to identify any tenderness or swelling. They may also perform specific movements to see if they elicit pain, which helps in pinpointing the inflamed bursae. In some cases, imaging tests like X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound may be ordered to rule out other conditions such as arthritis, hip deformities, or a strained muscle.
How Can Hip Bursitis be Successfully Treated by a Physiotherapist?
Physiotherapy is an effective way to manage and treat hip bursitis. A physiotherapist will develop a personalised treatment plan tailored to your specific needs. Here are some common physiotherapy interventions for hip bursitis:
1. Pain Management
Initial treatment focuses on reducing pain and inflammation. This may involve the use of ice packs, ultrasound therapy, or electrical stimulation. Your physiotherapist might also recommend over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications after consulting with your GP.
2. Manual Therapy
Manual therapy techniques, such as massage and joint mobilisations, can help alleviate pain and improve the range of motion. These hands-on techniques target the soft tissues and joints around the hip, promoting healing and reducing muscle tightness.
3. Activity Modification and Education
Your physiotherapist will educate you on modifying your activities to avoid aggravating the bursitis. They may suggest alternative exercises or movements that are less likely to strain the hip. Additionally, they will provide guidance on proper posture and ergonomics to minimise hip stress in daily activities.
4. Progressive Loading
As your symptoms improve, your physiotherapist will gradually increase the intensity of your exercises. Progressive loading helps strengthen the hip and surrounding muscles, enhancing your overall function and reducing the risk of recurrence.
5. Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
Stretching exercises can help improve the flexibility of the muscles around the hip, reducing pressure on the inflamed bursa. Strengthening exercises, particularly for the gluteal muscles and hip abductors, can help stabilise the hip joint and prevent further irritation. Here are some exercises you can try.
Clamshells
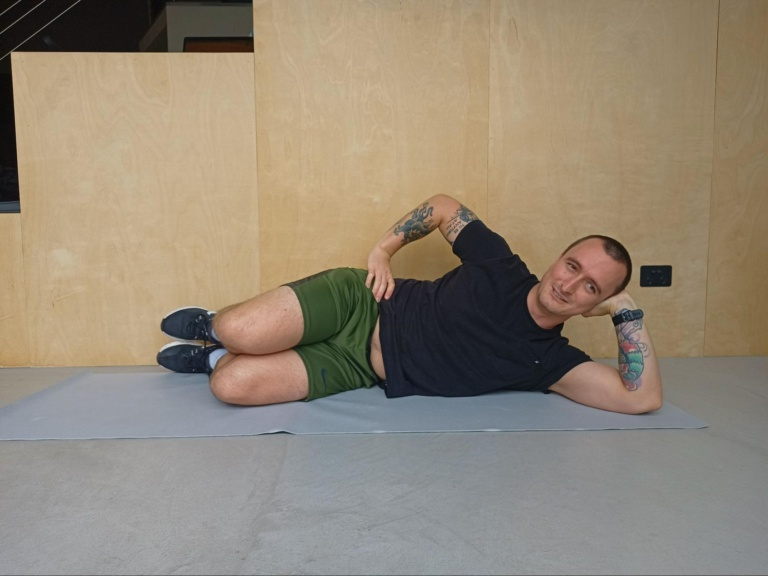
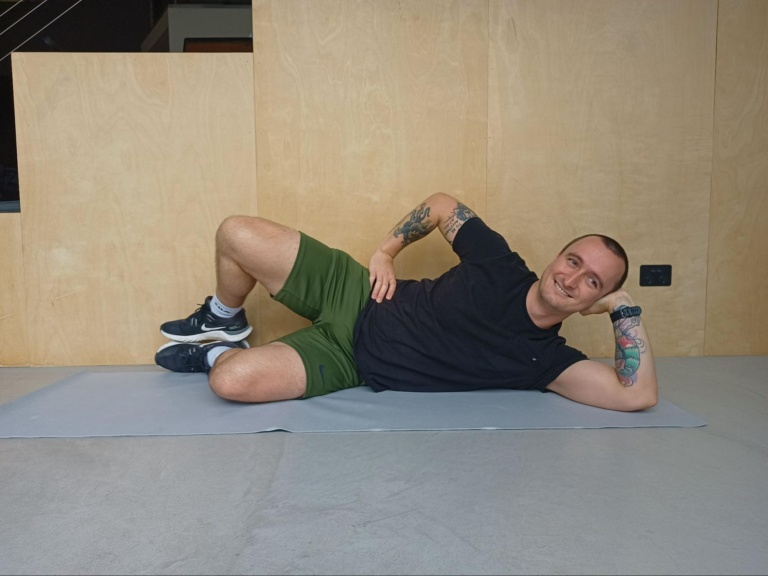


- Lie on your side with your knees bent at a 90-degree angle and your feet stacked on top of each other. Place one arm under your head for extra stability, the other arm can sit on the top of your hip or wherever feels comfortable.
- Slowly lift your top knee up towards the ceiling, keeping the feet together, until you feel the muscles. Hold this position for 5-10 seconds before slowly returning the knee to its starting point.
- Repeat this exercise 10-15 times for each leg.
- Aim to complete a full set of these 2-4 times per day for good results.
Lying Glute Stretch
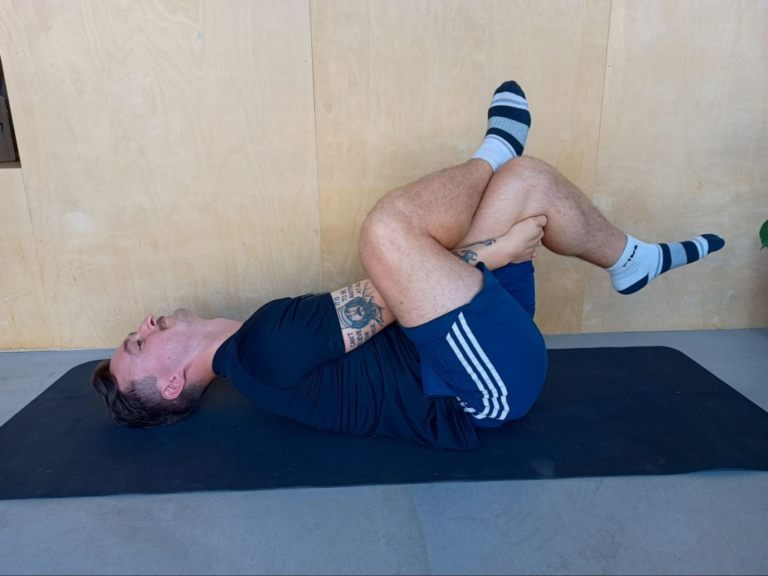

- Lie on your back on a flat surface, with both knees bent and feet flat on the ground.
- Cross one leg over the other by placing the ankle just above the knee on the opposite thigh.
- Gently pull the thigh of the uncrossed leg towards your chest, holding it either behind the thigh or on top of the knee.
- Hold the stretch for 20-30 seconds, feeling a gentle pull in the buttocks and hip of the crossed leg.
- Slowly release and switch legs to repeat the stretch on the other side.
- Ensure the stretch is comfortable and avoid any jerking or forceful pulling. This stretch should be a gentle, gradual extension, not a strain
Lying Hamstring Stretch
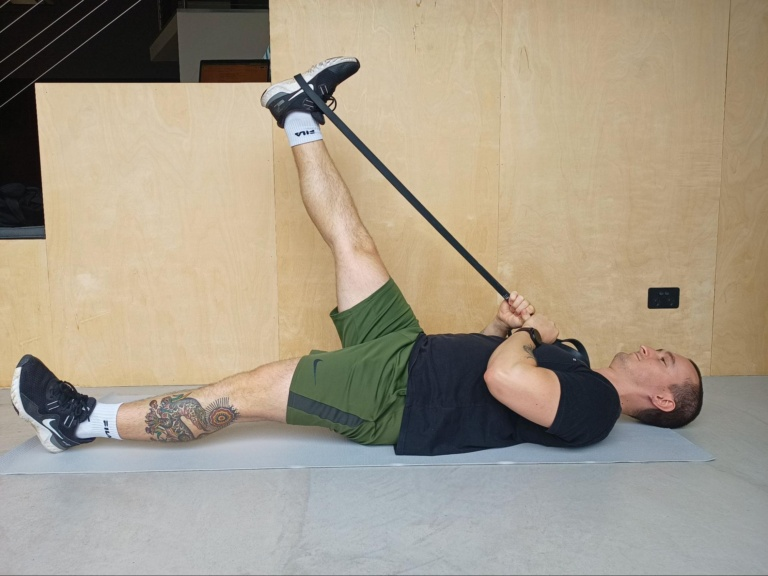

- Lie down on either the floor or a mat and extend both legs straight in front of you; if more comfortable, bend both knees with feet flat against the ground.
- Next, wrap a towel, belt, or band around the bottom of one foot.
- Straighten that leg and raise it into the air, pulling the wrap with your arms to help find a deep but comfortable stretch along the back of your leg.
- Hold that position for 30 seconds before lowering and switching sides.
- Aim to repeat each side 2-4 times as part of an effective workout routine!
Mini Squats
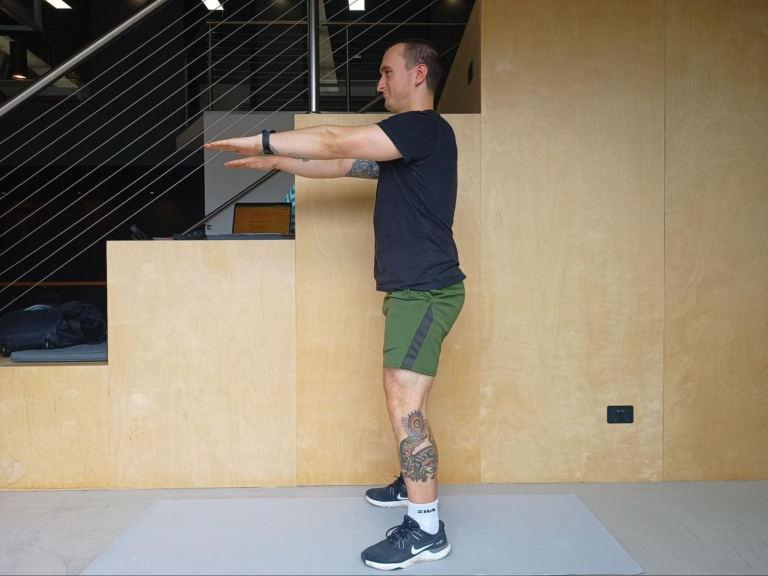
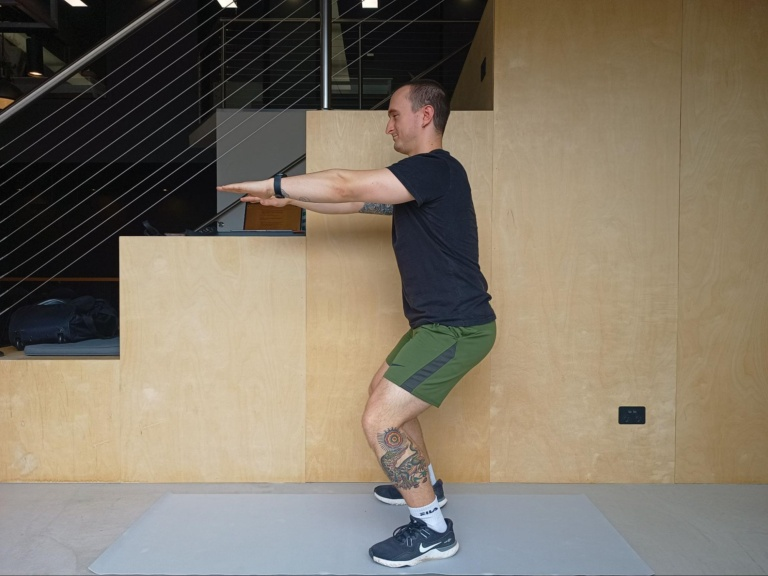


- Begin by standing with your feet hip-width apart, looking straight ahead, feet pointing forward.
- Keep your back straight, core tight, and chin up throughout the entire exercise.
- Lower yourself down as low as you can before the pain becomes too great.
- Push through your heels to lift yourself back up to starting position.
- Repeat 10-15 reps of this exercise 2-4 times a day, aiming to deepen your squat over time.
How Long Does it Take to Recover from Hip Bursitis?
Recovery time for hip bursitis depends on the severity of the condition and how well you adhere to your treatment plan. Mild cases of hip bursitis may resolve within a few weeks with appropriate physiotherapy interventions and self-care measures. More severe cases might take several months to fully heal.
It’s important to follow your physiotherapist’s recommendations and be patient with the recovery process. Consistency with exercises and modifications is key to achieving long-term relief from hip pain and preventing future episodes of bursitis.
Is There Anything I Can Do at Home to Help Relieve My Symptoms?
Yes, there are several self-care measures you can take at home to help relieve your symptoms of hip bursitis. Here are some tips:
1. Rest and Avoid Aggravating Activities
Give your hip ample rest and avoid activities that exacerbate the pain, such as prolonged standing, walking, or climbing stairs. Resting allows the inflammation to subside and prevents further irritation of the bursae.
2. Ice Therapy
Applying ice packs to the affected hip can help reduce inflammation and numb the pain. Use an ice pack for 15-20 minutes several times a day, especially after activities that increase your hip pain.
3. Gentle Stretching
Perform gentle stretching exercises like those listed above to maintain flexibility and reduce muscle tightness around the hip. Focus on stretches that target the hip flexors, quadriceps, and gluteal muscles. Remember to stretch slowly and avoid any movements that cause sharp pain.
4. Use of Cushions or Pads
When sitting, especially on hard surfaces, use cushions or pads to reduce pressure on the hip. This can help minimise discomfort and provide additional support to the affected area.
5. Anti-inflammatory Medications
Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications, such as ibuprofen, can help reduce pain and inflammation. However, always consult with your GP before taking any medications to ensure they are safe and appropriate for you.
6. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess body weight can put additional stress on the hip joints. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help reduce the burden on your hips and prevent further irritation of the bursae.
Disclaimer
Please consult your physiotherapist or GP prior to implementing any of the recommendations in this article. The information provided here is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice or treatment.
By following the guidance of a skilled physiotherapist and incorporating these self-care measures, you can effectively manage hip bursitis and alleviate hip pain. Remember, early intervention and adherence to your treatment plan are crucial for a successful recovery. If you experience persistent or worsening symptoms, seek medical attention promptly to ensure appropriate care and prevent complications.
By providing a comprehensive approach to understanding, diagnosing, and treating hip bursitis, we hope this blog has shed light on how physiotherapy can be a powerful tool in managing this common condition. For those experiencing hip pain, consulting with a physiotherapist can pave the way for effective relief and a return to normal activities.